What is Retail Arbitrage?
First things first, let’s find out what is retail arbitrage? It is a popular method of making money, particularly on Amazon. It involves buying discounted products from physical stores like Target or Walmart and reselling them for a higher price on Amazon. This practice is often referred to as Amazon arbitrage. Those who excel at retail arbitrage have a knack for finding heavily discounted items and turning them into profitable sales.
Online arbitrage is a similar concept, but instead of buying from physical stores, you purchase products from online retailers. Both retail and online arbitrage offer exciting opportunities for savvy shoppers to earn extra income by leveraging price differences across various marketplaces.
An example can help you understand retail arbitrage meaning better. Let’s say you visit your local Walmart and find a clearance sale where a popular brand of kitchen appliances, like blenders, is significantly discounted. Normally, these blenders retail for $50, but Walmart has marked them down to $15 to clear out inventory. Recognizing an opportunity, you purchase ten of these blenders for a total of $150. Next, you list each blender on Amazon for $45, a price lower than the typical retail price but high enough to make a good profit.
Once all ten blenders sell on Amazon, you earn $450 in total revenue. After subtracting the initial $150 spent on purchasing the blenders and accounting for Amazon’s selling fees (let’s say $5 per blender, totaling $50), you end up with a net profit of $250.
Pros & Cons of Retail Arbitrage
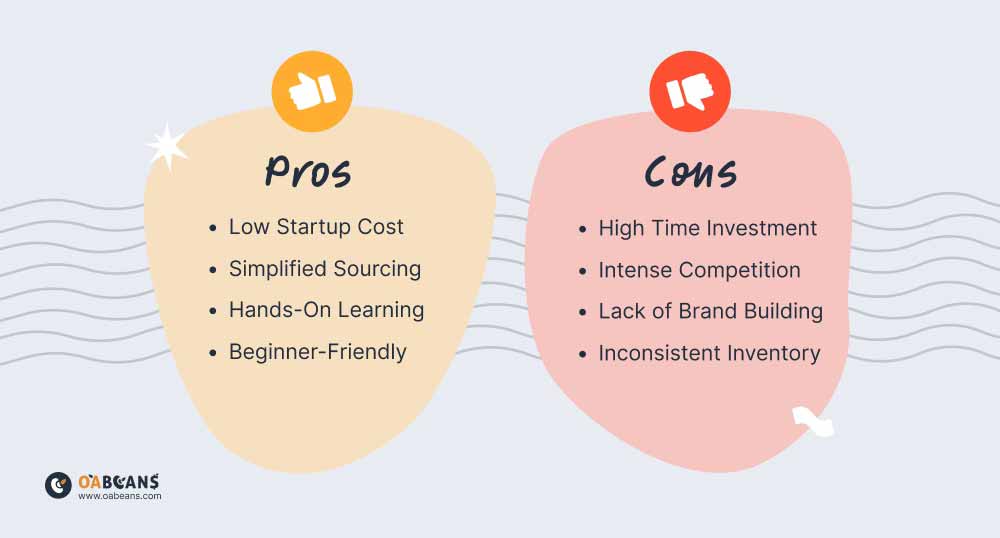
No selling strategy is perfect, and each business model has its own advantages and disadvantages. With that said, here are the pros and cons of retail arbitrage:
Pros:
- Low Startup Cost: When you’re doing retail arbitrage, you can buy as much or as little as you can afford. Unlike dealing with suppliers who often have minimum order quantities, you can start with just a few dollars.
- Simplified Sourcing: Sourcing and dealing with overseas suppliers can be overwhelming, especially for beginners. With retail arbitrage, you simply buy from local stores, eliminating the complexity of supplier negotiations.
- Hands-On Learning: Retail arbitrage helps you learn the ropes of selling on Amazon. You’ll gain experience in creating listings, collecting reviews, and more. This knowledge will be invaluable if you later decide to source products from suppliers or manufacturers.
- Beginner-Friendly: With its low budget requirements and simplicity, retail arbitrage is an ideal business model for beginners. You can easily test the waters by buying a few items from your local store and reselling them online.
Cons:
- High Time Investment: Driving from store to store looking for deals takes a lot of time. While this strategy can be profitable, it often requires more time investment compared to placing bulk orders from a supplier.
- Intense Competition: Many of the items you sell will already be listed on Amazon, meaning you’ll share the buy box with other sellers. This increased competition can make it harder to sell your products and maintain profitable margins.
- Lack of Brand Building: Building a brand is difficult when you’re reselling other people’s products. To grow a loyal customer base and establish a strong brand presence, you’ll eventually need to work with a manufacturer to create a private label product that no one else offers.
- Inconsistent Inventory: The availability of profitable products can be inconsistent. You might find a great deal one week but struggle to find similar opportunities regularly. Stores may sell out of discounted items or raise their prices, making it harder to maintain a steady inventory.
How to Start Doing Retail Arbitrage?
Retail arbitrage can be performed on any online marketplace, but the most popular platform for this strategy is Amazon. Here are seven steps to Amazon arbitrage for beginners:
1. Sign Up for an Amazon Seller Account
Before you can start selling on Amazon, you need to register for a seller account. You have two options: a Professional Seller account or an Individual Seller account.
- Professional Seller Account: Costs $39.99 per month but waives the $0.99 fee per sale. Ideal if you plan to sell more than 40 items a month.
- Individual Seller Account: Free to have but charges an additional $0.99 for each sale. Suitable if you expect to sell fewer than 40 items a month.
To sign up, you’ll need to provide Amazon with a piece of ID, a credit card, and your tax information. Follow the directions to complete the application process.
2. Visit Local Retailers & Do Product Research
It’s crucial to do some product research before you start shopping. This ensures you don’t end up buying products with no demand on Amazon. Use tools like Keepa and other resources to define the best items for retail arbitrage, allowing you to make smarter purchasing decisions.
You can find good deals at local stores, especially those that are moving or closing and need to liquidate their inventory. Some of the top retail arbitrage stores include Walmart, Home Depot, Target, and other similar stores.
3. Scan Products
Use the Amazon Seller App while shopping to check what an item is selling for on Amazon. Simply download the app and scan products with your smartphone to see the sales price. Look for items selling for half or less of their price on Amazon.
Aim for products that yield at least $3 in profit after expenses. This may mean looking for higher-ticket items to ensure profitability after Amazon fees and shipping costs.
4. Determine Whether You Can Sell the Product
Some brands and categories are restricted on Amazon, requiring special approval or being completely off-limits. Avoid buying inventory you can’t resell by steering clear of restricted brands and categories. Examples of restricted brands include:
- Adidas
- Birkenstock
- Crocs
- Dell
- HP
- iPhone
Examples of restricted categories include:
- Collectible Coins
- Personal Safety and Household products
- Entertainment Collectibles
- Fine Art
- Gift Cards
- Jewelry
5. Decide How Much to Buy

Consider the following when deciding how much inventory to purchase:
- Profit Potential: More inventory can mean more profit but also more risk.
- Affordability: Stick to your budget to avoid financial strain.
- Availability: The supply of the item may be limited.
- Product Proven Success: Start with a small quantity to test the market if you’re unsure about the product’s potential.
6. List Your Items on Amazon
Create your Amazon listings through your Seller Central account. If your product is already sold on Amazon, it will be added to an existing listing. If not, you’ll need to create a new listing.
7. Choose Your Fulfillment Option
Choosing the FBA (Fulfilled by Amazon) option for your retail arbitrage business can provide significant advantages. When you opt for FBA, you send your purchased products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, where they handle storage, packing, shipping, and customer service on your behalf (as opposed to FBM or Fulfilled by Merchant, where you handle everything yourself).
FBA also enables your products to be eligible for Amazon Prime benefits, offering faster shipping and enhanced visibility on the platform. Prime-eligible products often receive preferential treatment in search results and can attract more potential customers.
8. Assess Profit Margins
To determine your actual profit from retail arbitrage, it’s crucial to calculate the net profit after deducting Amazon’s fees and other costs. Amazon charges various fees, such as referral fees, fulfillment fees, and storage fees, which are associated with selling on their platform. It’s important to consider these fees when setting your selling price to ensure a healthy profit margin.
Remember to regularly reassess and analyze your profitability to adjust your sourcing and pricing strategies accordingly. This will help you optimize your business and maximize your profits.
9. Monitor Reviews and Manage Your Platform
Customer reviews play a crucial role in your success as a seller. Respond to reviews promptly, and strive to offer exceptional service to receive positive reviews. Keep an eye on your competitors’ reviews to gauge their performance and make necessary adjustments to your selling strategy.
Advanced Data & AI Integration: Transforming Retail Arbitrage in 2025 with AI-Powered Sourcing, Pricing, and Enhanced Analytics Tools
In 2025, the landscape of retail arbitrage has been revolutionized by advanced data analytics and cutting-edge artificial intelligence integration. AI-powered sourcing and pricing now enable sellers to analyze vast datasets rapidly, predict market trends with unprecedented accuracy, and optimize pricing strategies for maximum profitability. Enhanced analytics tools like updated versions of Keepa and Tactical Arbitrage deliver predictive insights, automated repricing capabilities, and granular market data, empowering sellers to streamline inventory management and stay ahead of fierce competition. This breakthrough technology transforms decision-making, reduces risk, and significantly improves operational efficiency in the dynamic retail arbitrage market of 2025 for unstoppable success.
How to Source Retail Arbitrage Products to ReSell on Amazon?
Retail arbitrage products can be sourced from various locations. Here are some common places for Amazon product sourcing:
- Big-Box Retailers: Stores like Walmart, Target, Home Depot, Lowe’s, and Best Buy often have clearance sections or discounted items that can be purchased at a lower price and resold for a profit.
- Department Stores: Retailers like Macy’s, Kohl’s, JCPenney, and Nordstrom occasionally offer sales, promotions, or clearance events where products can be sourced for resale.
- Local Grocery Stores: Supermarkets and grocery stores may have clearance aisles or discounted items, including non-perishable goods, household items, and health and beauty products.
- Drugstores: Pharmacies and drugstores like CVS, Walgreens, and Rite Aid often have sales or clearance sections where items such as cosmetics, personal care products, and over-the-counter medications can be sourced.
- Discount Stores: Discount retailers like Marshalls, Ross, T.J. Maxx, and Big Lots offer discounted merchandise, including clothing, home goods, and electronics, which can be resold for a profit.
- Thrift Stores: Thrift stores, consignment shops, and second-hand stores can be treasure troves for finding unique or vintage items at low prices that can be resold for a profit.
- Liquidation Sales: Businesses that are closing or liquidating their inventory may offer steep discounts on merchandise, providing opportunities for retail arbitrage.
- Local Retailers: Explore local boutique stores, independent retailers, flea markets, and clearance sales in your area for potential arbitrage opportunities.
- Seasonal Sales: Take advantage of seasonal sales events such as Black Friday, Cyber Monday, holiday clearance sales, and end-of-season markdowns to find discounted products for resale.
Types of Products to ReSell on Amazon
When it comes to reselling products on Amazon through arbitrage, sellers often gravitate towards certain categories that consistently perform well. Here are the top 10 favorite categories in Amazon arbitrage for beginners:
- Home & Kitchen: With 25% of retail arbitrage sellers favoring this category, it’s a popular choice for sourcing products like kitchen gadgets, home decor, appliances, and organizational items.
- Cell Phone & Accessories: Coming in second at 18%, this category includes items such as phone cases, screen protectors, chargers, and other mobile accessories that appeal to a wide audience.
- Electronics: Also at 18%, electronics offer opportunities for reselling items like headphones, Bluetooth speakers, smart home devices, and gadgets that are in high demand among consumers.
- Arts, Crafts & Sewing: With 16% of retail arbitrage sellers focusing on this category, products such as art supplies, crafting tools, sewing kits, and DIY materials attract both hobbyists and professionals alike.
- Grocery & Gourmet Food: Also at 16%, this category encompasses a variety of food and beverage products, including snacks, gourmet treats, pantry staples, and specialty items that are popular among consumers.
- Toys & Games: With 14% of retail arbitrage sellers choosing this category, toys, board games, puzzles, action figures, and educational toys offer lucrative opportunities, especially during peak shopping seasons.
- Appliances: At 12%, appliances like small kitchen appliances, home electronics, and household gadgets provide practical and in-demand products for resale.
- Beauty & Personal Care: With 11% of retail arbitrage sellers focusing on this category, beauty products, skincare items, hair care products, and personal care essentials appeal to a broad consumer base.
- Books: Also at 11%, books remain a popular choice for resale, including both fiction and non-fiction titles, textbooks, cookbooks, and niche publications.
- Sports & Outdoors: At 9%, sports equipment, outdoor gear, fitness accessories, and recreational products cater to active lifestyles and outdoor enthusiasts.
Best Retail Arbitrage Tools & Software
Retail arbitrage can be made significantly easier and more profitable with the right tools. Here are six of the best tools that can help in Amazon arbitrage for beginners:
1. Keepa
Keepa is a powerful tool for tracking the price history of products on Amazon and it is considered one of the best retail arbitrage tools. It provides detailed charts that show historical pricing, sales rank, and any fluctuations. This data helps arbitrage sellers understand market trends, price stability, and the best times to buy and sell products.
Features:
- Price tracking and alerts
- Sales rank history
- Product availability alerts
- Browser extensions for easy access
You can check out our Keepa reviews article to get more familiar with this tool.
2. Tactical Arbitrage
Tactical Arbitrage is a comprehensive tool designed specifically for retail and online arbitrage. It allows users to scan thousands of products across various online and brick-and-mortar retailers and compare prices with Amazon listings to identify profitable arbitrage opportunities.
Features:
- Product sourcing from multiple online and brick-and-mortar retailers
- Advanced filters and search parameters
- Profitability and ROI calculations
- Integrated product scanner
Make sure to check out our Tactical Arbitrage reviews for more info!
3. RevSeller
RevSeller is a browser extension that integrates directly into Amazon’s product pages, providing vital information at a glance. It offers quick calculations for fees, profit margins, and ROI, making it easier to evaluate the profitability of products during sourcing.
Features:
- Real-time profit and ROI calculations
- FBA fee breakdowns
- Sales rank and category data
- Quick ASIN lookup
If you want to know more about this tool, you can check out our RevSeller reviews.
4. ScanPower
ScanPower is a suite of tools designed for Amazon sellers, focusing on scanning, listing, and repricing products. It helps sellers streamline their sourcing process and manage their inventory effectively.
Features:
- Mobile app for scanning products in stores
- Profitability analysis and ROI calculations
- Inventory management tools
- Repricing tools to stay competitive
5. Profit Bandit
Profit Bandit is a mobile app that allows sellers to scan barcodes of products in retail stores and instantly see if they can make a profit reselling them on Amazon. It provides critical data on pricing, fees, competition, and sales rank.
Features:
- Barcode scanning and product lookup
- Real-time profit and fee calculations
- Sales rank and competition analysis
- Customizable alerts and settings
6. BrickSeek
BrickSeek is a tool that helps find clearance deals and discounts at major retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot. It allows users to search for products and see their availability and prices at local stores.
Features:
- Inventory and price checker for major retailers
- Local availability and stock alerts
- Historical price data and trends
- Deal alerts and notifications
Best Ways to List Retail Arbitrage Products on Amazon
Creating a listing for retail arbitrage on Amazon involves a few straightforward steps. Since you’re not selling a private label product, you don’t need to create a brand-new listing. Instead, you can find the existing listing that matches your product and add its unique ASIN to your catalog in Seller Central. Here’s how you can do it:
Option 1: List the Item from the Amazon Seller App
- Scan the Product: Use the Amazon Seller App to scan the product you want to sell.
- Select Fulfillment Method: Decide whether you will fulfill the order yourself (FBM) or use Amazon’s fulfillment service (FBA).
- List the Item: Tap the “List” button located in the bottom right-hand corner of the app. Enter the product’s condition (usually “New”), price, SKU, and fulfillment channel.
- Set Pricing: Be careful with pricing. Although Amazon may suggest “Match Low Price,” it’s crucial to check the FBA prices. The lowest FBM price might not be profitable for you. Aim for the lowest FBA price to maintain profitability. You can always adjust the price once your inventory is ready for sale from an FBA warehouse.
- Customize SKU: Create a custom SKU to track the cost and origin of the product. For example, if you bought chalk at Walmart for $5.75 and your breakeven price is $14.00, you could format your SKU as WM_5.75_BE14.
- Select Fulfillment Channel: Choose “I will ship this item myself” for FBM and enter your inventory in the app. Or, choose “Amazon will ship and provide customer service” for FBA. This will add the listing to Seller Central, and you’ll need to create an FBA shipment there (more on that later).
Option 2: List in Seller Central on Your Desktop/Laptop
- Find the Listing: Locate the existing listing on Amazon that matches the product you want to sell.
- Copy the ASIN: Copy the ASIN of the product.
- Add the Product: Go to Seller Central, then navigate to Inventory > Add a product. Paste the ASIN into the search bar and find the product. Select the product’s condition as “New” and click “Sell this product.”
- Save and Finish: After pressing “Save and finish,” Amazon will create a listing that will appear on your Manage Inventory page. It may take about 15 minutes for the listing to become searchable.
- Create a Shipment: Once the listing is active, you’ll need to create a shipment in Seller Central to send your inventory to an Amazon warehouse.
How to Create FBA Shipment for Retail Arbitrage?
Creating a shipment for retail arbitrage on Amazon is the next step after purchasing your inventory and adding the listings in Seller Central. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process of retail arbitrage for beginners:
Step 1: Find Your Product in Manage Inventory
- Locate the Product: Go to your Seller Central account and navigate to the “Manage Inventory” section.
- Select Send/Replenish Inventory: In the “Edit” drop-down menu on the far right of the product listing, select “Send/Replenish Inventory.”
Step 2: Choose What Inventory You Want to Send
- Edit Packing Template:
- Template Name: You can give your packing template a specific name for easy reference.
- Units per Box: Enter the number of units you will pack in each box.
- Box Dimensions and Weight: Provide the dimensions and weight of each box.
- Prep Needed: Indicate if any special preparation is needed for the items.
- Choose Number of Boxes: Specify how many boxes you are sending to Amazon. For example, you might send 1 box filled with 20 units.
- Confirm and Continue: Once all details are entered, click “Confirm and continue.”
Step 3: Confirm Shipping
- Set Ship Date: Choose the date you plan to ship your inventory.
- Select Shipping Mode: Choose your shipping method, such as “small parcel delivery” for smaller shipments.
- Review Inbound Shipping Price: Amazon will provide the shipping cost if you’re using their partnered carrier (e.g., UPS), which typically offers discounted rates. For example, a 15-pound shipment might cost only $8.69.
- Accept Charges: If you agree with the shipping costs, click “Accept charges and confirm shipping.”
Step 4: Print FBA Labels
- Print Labels: After confirming the shipment, print the FBA label. The label will include two barcodes: one for UPS (or your chosen carrier) and one for Amazon, which identifies the sender and the contents of the shipment.
- Affix Labels: Ensure both barcodes are visible on the outside of your box for easy scanning by UPS and Amazon.
Extra Tips for Pro Retail Arbitrageurs
Learning retail arbitrage for beginners can be rewarding, but it requires diligence, strategic planning, and informed decision-making. Here are some essential tips to help you succeed:
- Product Reviews: Investigate customer demand by reading reviews (or checking them on tools like Keepa), particularly recent ones. A lack of frequent, recent reviews could indicate low interest in the product.
- Sales Ranking: Use the Amazon Seller App to check the sales ranking of potential products. Aim for products that rank below 250,000 to minimize competition.
- Profit and ROI: Look for products that offer at least a $5 potential profit margin and a 20%-10% return on investment (ROI) after considering sales taxes, Amazon fees, and shipping costs.
- Quantity Control: Avoid purchasing large quantities of any product to prevent getting stuck with unsellable inventory. Start small and scale up as you become more familiar with the market.
- Avoid Competing Directly with Amazon: Amazon often wins on price and brand recognition. Instead, focus on products where you can offer unique value.
- Sign Up for Retailer Newsletters: Get advance notice of coupons and exclusive deals that aren’t available to regular customers.
- Use Tools and Apps: Leverage the Amazon Seller App and tools like Tactical Arbitrage to make informed buying decisions. Analyzing data helps avoid purchasing products that won’t sell.
- Monitor Price Changes: Be aware that prices can change quickly if another seller lowers their price. Check price history and keep an eye on the market to make informed pricing decisions. You can also use repricer tools to automate this process.
- Plan for Seasonal Products: Research and plan for products that sell well during specific times of the year. For example, toys are in high demand during the holiday season, while inflatable pools are popular in the summer.
- Source Rare Items: Look for discontinued products that are still in circulation. These can often be found in local stores, discount outlets, and grocery stores.
- Check for Restrictions: Be aware of any restrictions associated with certain products. Some items may be prohibited or have limitations imposed by the manufacturer. Use the Amazon app to check for restrictions before purchasing.
Other Amazon Business Models
Amazon provides a diverse marketplace for entrepreneurs, accommodating various business models, each with its own set of characteristics and potential for success. Here are some of the most popular Amazon business models:
1. Dropshipping
Dropshipping involves selling products without holding inventory. Sellers list items on Amazon, and when a customer places an order, the seller forwards it to a supplier. The supplier then handles the packaging, shipping, and after-sale services. Make sure you read our Amazon FBA or Dropshipping comparison to know which business model is best for you.
2. Private Labeling
Private labeling involves sourcing existing products and rebranding them under your own brand. Sellers can slightly modify the product or completely change its design, allowing them to sell proven products under a unique brand name. We compared retail arbitrage vs. private label in a different article to give you a general idea of what each business model entails.
3. Wholesale
The wholesale model involves purchasing products in bulk directly from brands or distributors and reselling them on Amazon. Sellers become authorized resellers, ensuring product authenticity and maintaining steady inventory levels. You can read our retail arbitrage vs. wholesale article to determine which business model suits you best.
4. Handmade Products
Handmade products are crafted by the seller and sold on Amazon. This model has gained popularity, with the number of active handmade product producers on Amazon increasing by almost 750% over the past five years.
Conclusion
Retail arbitrage is a great way for new entrepreneurs to start an Amazon business with little upfront cost. By buying discounted products from stores and selling them on Amazon, you can make a profit from the price difference. To succeed, you need to research products well, keep track of prices, and understand Amazon’s fees and rules. Using tools like the Amazon Seller App and staying aware of market trends can help you stay competitive. Start small, be patient, and learn as you go to build a successful and profitable business on Amazon.
Yes, but why is retail arbitrage legal? It is legal because it involves buying products from retail stores and reselling them at a higher price, a practice supported by the First Sale Doctrine and ownership rights.
No, they are similar but not the same. But what is the difference between retail arbitrage vs online arbitrage? Retail arbitrage involves buying products from physical stores, while online arbitrage involves purchasing products from online retailers.
Many people ask, is retail arbitrage dead? Is it still profitable in 2025? Yes, retail arbitrage can still be profitable in 2025. However, success depends on effective product research, competitive pricing, and understanding market trends.
















12 responses to “Retail Arbitrage for Beginners in 2025”
Sorry I didn’t understand the differences of online and retail arbitrage.
Great article. Thanks OABeans.
helpful to start my online business
I appreciate the option to subscribe to products on Amazon Marketplace – it’s a hassle-free way to receive products regularly.
Your website emphasizes the importance of steady and consistent growth rather than quick wins, providing guidance on planning for the long-term success of an Amazon FBA business.
I love how you give examples and real-life scenarios to explain your points. This makes your site relatable and practical.
Reselling on Amazon is a great way to turn your passion for entrepreneurship into a successful venture. With persistence and perseverance, you can achieve your business goals.
Amazon’s massive customer base and global reach provide a ready market for your retail arbitrage finds. You can tap into a wide audience and increase your sales potential.
The FBA program offers excellent customer service, handling returns and inquiries on your behalf, ensuring a seamless buying experience.
With online arbitrage, you can adapt to market demand and quickly adjust your product sourcing strategies to meet customer preferences.
Reselling on Amazon offers a low-risk and accessible business opportunity, where you can start with minimal investment and gradually grow your business.
A big thank you for your article.Really thank you! Cool.